Effective Methods
of Contraception
There are many methods of
contraception out there, but how many are more likely to prevent pregnancy? The
methods available are not only for women, but for men too. The top five
effective methods of contraception are male sterilization, female sterilization,
contraceptive implant, IUD, and Depo-Provera (Lehmiller, pg.264).
First we will start with male
sterilization. Male sterilization is a procedure that will permanently keep him
from being able to get a woman pregnant. The procedure is done by a health care
provider who will make tiny cuts in the scrotum. The tubes that carry the sperm
are then tied off and cut. A fluid (semen) will still come out of the penis; it
just won’t contain any sperm. This can be great because it is something that is
completely controlled by him. It can be upsetting if he or the couple
eventually change their mind and decide they want to have children, because
this procedure lasts the rest of their life.
Female sterilization is a procedure
that will permanently keep her from becoming pregnant. The procedure can be
done two ways, one is surgical and the other is non-surgical. In surgical sterilization
the fallopian tubes are cut, and then sealed or tied. In the non-surgical
sterilization a small coil is placed into each fallopian tube. The coil then
causes scar tissue to form in the tubes, which blocks them. If one chooses the
non-surgical method, it will take up to three months for the scar tissue to
fully block the tubes. This option like male sterilization is great because it
is safe/effective, and it is something that can be controlled by her. However, this
surgery lasts a life time, and if they change their mind it can be devastating.
 |
| http://www.sparrow.org/HealthLibrary/MayoContent /global//images/image_popup/mcdc7_implanon.jpg |
Contraceptive implants such as
implanon and nexplanon are about the size of a match, and it is inserted in the
arm to prevent pregnancy. They work by releasing a small amount of hormone into
the body, which prevents the body from releasing eggs, and also changes the
mucus of the cervix to make it harder for sperm to enter. This method is great
because it goes into the upper arm and lasts for up to three years. It is not
permanent, and can be removed by a health care provider at any time.
 |
| http://www.conceiveeasy.com/uploads /risks-of-an-iud-pregnancy.png |
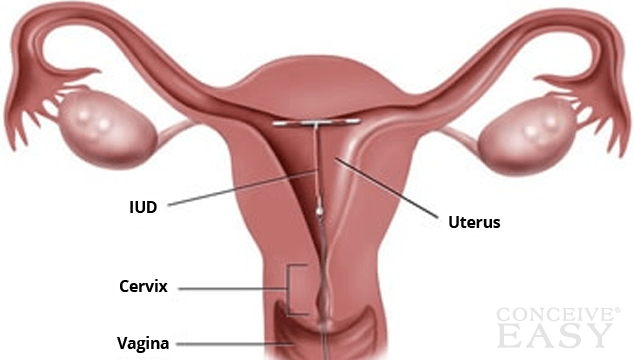
An IUD is a small T-shaped device
that is made of soft, flexible plastic. There are currently two types available
in the United States. ParaGard is a copper IUD made up of copper and plastic,
it prevents pregnancy by blocking the sperm from meeting with and fertilizing
an egg. Mirena also works by stopping the sperm from meeting with and
fertilizing an egg. The mirena also prevents pregnancy by releasing a small
amount of progestin which prevents the ovaries from releasing an egg. The IUD
is inserted into the uterus by a health care provider, and it is effective for
about five to ten years.
 |
| http://www.feministcenter.org/assets/images/ birth-control/133x150xshot.jpg.pagespeed.ic.VVXOktxe4g.jpg |
Depo-Provera is an injection of the
hormone progestin. This prevents pregnancy by keeping the ovaries from
releasing eggs. The shot also causes the cervical mucus to thicken, which
blocks sperm from meeting with and fertilizing an egg. Each injection lasts for about 12 weeks, and
it is important that the shot is given on time every time to prevent pregnancy.
An interesting fact about the shot is that women who take the shot are less
likely to have cancer of the uterus and pelvic inflammatory disease. If a woman
decides that she wants to get pregnant, it may take up to a year after stopping
the injection to become pregnant. Another interesting fact about the shot is
that using it longer than two years may cause the bones to thin and it can
worsen over time. Normal bone growth returns when she stops taking the shot.
There are many more methods of
contraception than I mentioned here. There are a few more that are close to the
effectiveness as the ones mentioned above. They are; male condom, oral contraceptives,
contraceptive patch, and the vaginal ring. The effectiveness of any contraception
depends on the user, and if they are using them correctly. I encourage those of
you who are interested in the different types of contraception to research them
and figure out what works best for you.
References
Birth Control Implant (Implanon and Nexplanon) :: Planned
Parenthood. (n.d.). Birth
Control Implant (Implanon and Nexplanon) :: Planned Parenthood. Retrieved
June 28, 2014, from
http://www.plannedparenthood.org/health-info/birth-control/birth-control-implant-implanon
Lehmiller, J. J. (2014). Sex Education, Contraception, and
pregnancy. The
psychology of human sexuality (p. 264). Oxford: John Wiley &
Sons.
Office of Population Affairs (OPA). (n.d.).Shot. Retrieved
June 28, 2014, from
http://www.hhs.gov/opa/reproductive-health/contraception/shot/
Office of Population Affairs (OPA). (n.d.).Female
Sterilization. Retrieved June 28, 2014, from http://www.hhs.gov/opa/reproductive-health/contraception/female-sterilization/
Office of Population Affairs (OPA). (n.d.).IUD.
Retrieved June 28, 2014, from http://www.hhs.gov/opa/reproductive-health/contraception/iud/
Office of Population Affairs (OPA). (n.d.).Male
Sterilization. Retrieved June 28, 2014, from
http://www.hhs.gov/opa/reproductive-health/contraception/male-sterilization/
No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.